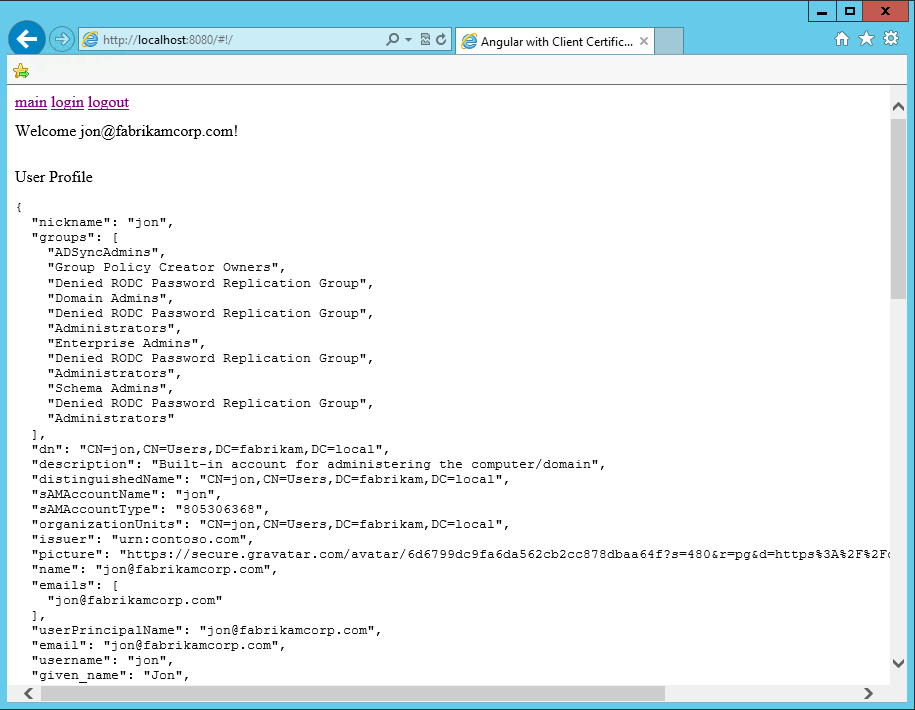
Enable client certificates
- Go to Auth0 Dashboard > Authentication > Enterprise > Active Directory/LDAP, and select the connection you want to configure.
- Toggle the Use client SSL certificate authentication option in the settings.
- Provide IP address ranges in the IP Ranges field. Only users coming from the given IP ranges are prompted to authenticate using client certificates. Users from different IP ranges are prompted to login with the username and password login form.
Configure certificates
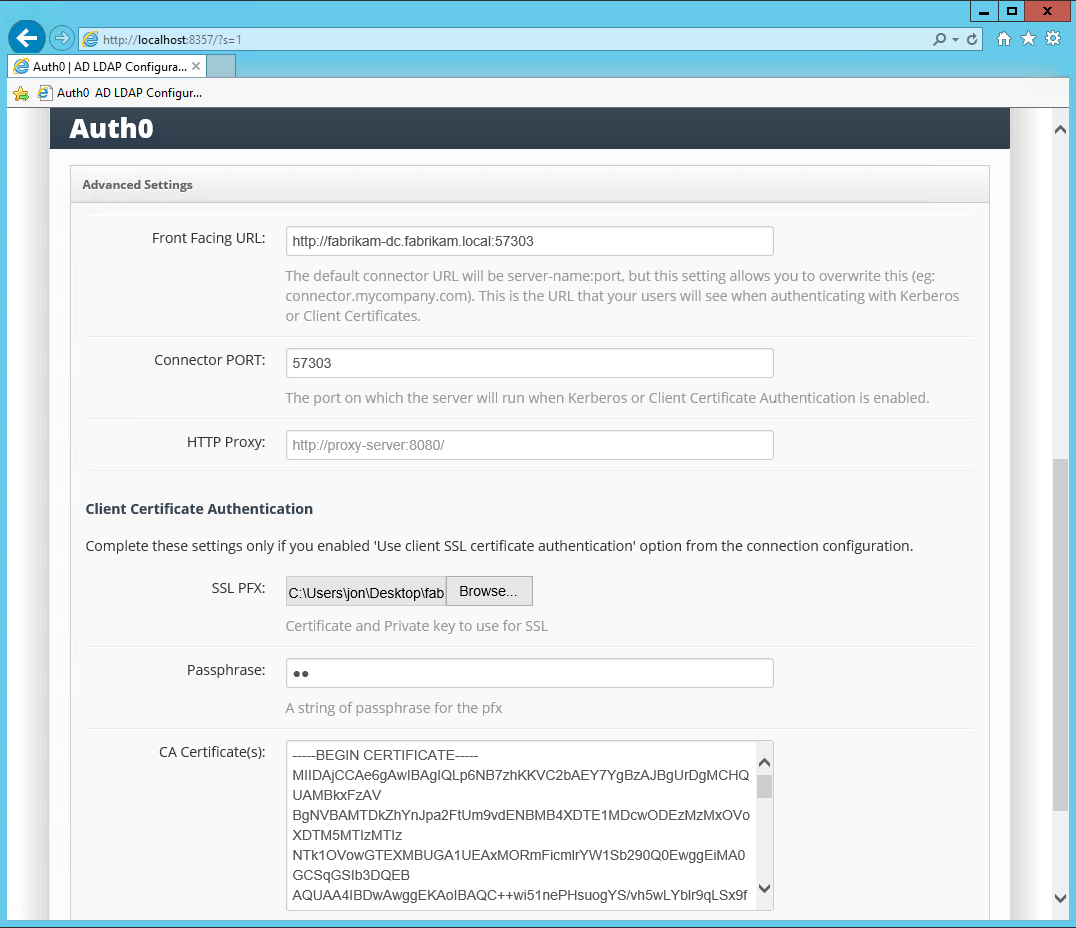
Once the AD/LDAP connection has been configured in Auth0, you’ll need to configure the certificates in the AD/LDAP Connector. Supporting client certificates will require the following:- An SSL certificate for the Front Facing URL, because the interaction between the end user and the Connector will need to happen over HTTPS.
- One or more CA certificates.
- A Client Certificate signed by the CA for each user that needs to authenticate using Client Certificates.
- Before uploading certificates to the AD/LDAP connector, convert X.509 certificates to Base64. Use Base64 or Certutil on Windows Server. To learn more, see Base64 Decode at Base64decode or Certutil.exe in Microsoft documentation.
-
Upload the SSL and CA certificates to the AD/LDAP Connector:
-
To test, generate a self-signed CA and Client Certificates using makecert.exe on Windows, which is part of the Windows SDK:
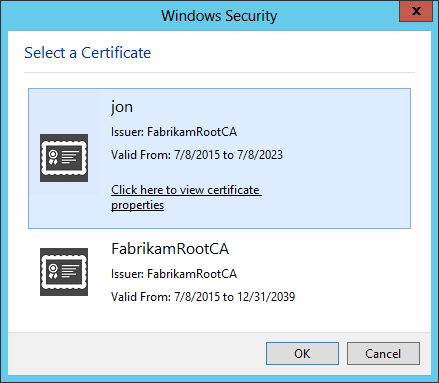
It is important that the Client Certificate’s subject be in the format of
CN=AD_USERNAME, for exampleCN=jon.