This guide demonstrates how to integrate Auth0 with any new or existing Express.js API application using the
express-oauth2-jwt-bearer package.If you have not created an API in your Auth0 dashboard yet, use the interactive selector to create a new Auth0 API
or select an existing project API.To set up your first API through the Auth0 dashboard, review our getting started
guide. Each Auth0 API uses the API Identifier, which your application needs to validate the access token.New to Auth0? Learn how Auth0 works
and read about implementing API authentication
and authorization using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
1
Define permissions
Permissions let you define how resources can be accessed on behalf of the user with a given access token. For
example, you might choose to grant read access to the 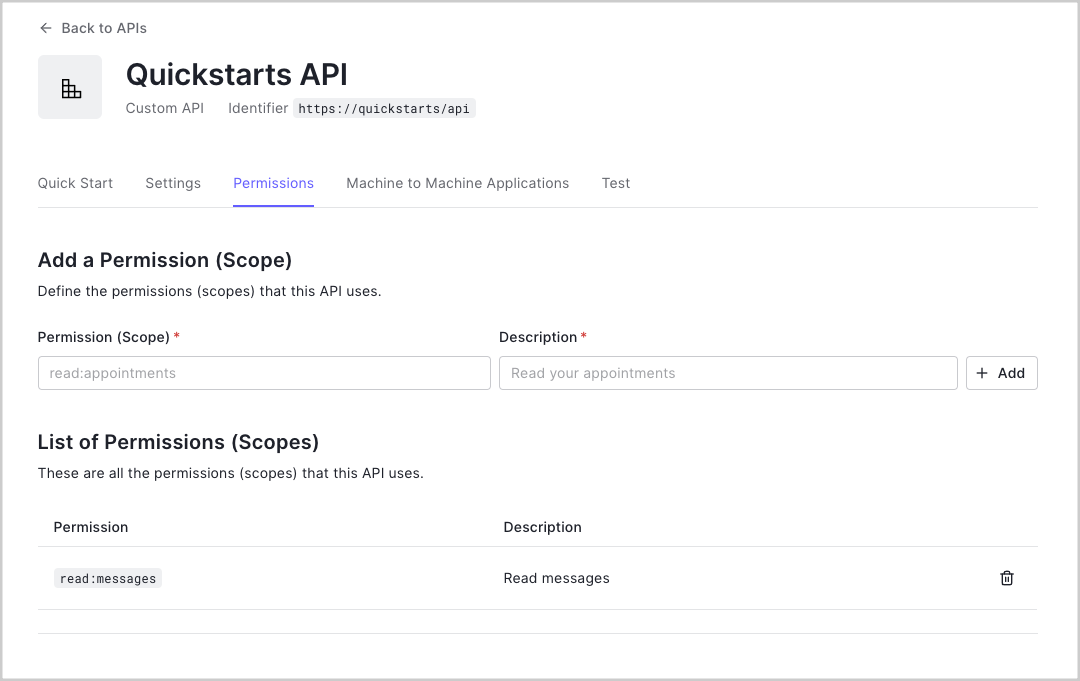
messages resource if users have the manager
access level, and a write access to that resource if they have the administrator access level.You can define allowed permissions in the Permissions view of the Auth0 Dashboard’s APIs section.
This example uses the
read:messages scope.2
Install dependencies
First, install the SDK with
npm.3
Configure the middleware
Configure
express-oauth2-jwt-bearer with your Domain and API Identifier.The checkJwt middleware shown to the right checks if the user’s access token included in the request
is valid. If the token is not valid, the user gets a 401 Authorization error when they try to access the
endpoints.The middleware does not check if the token has sufficient scope to access the requested resources.4
Protect API endpoints
To protect an individual route by requiring a valid JWT, configure the route with the 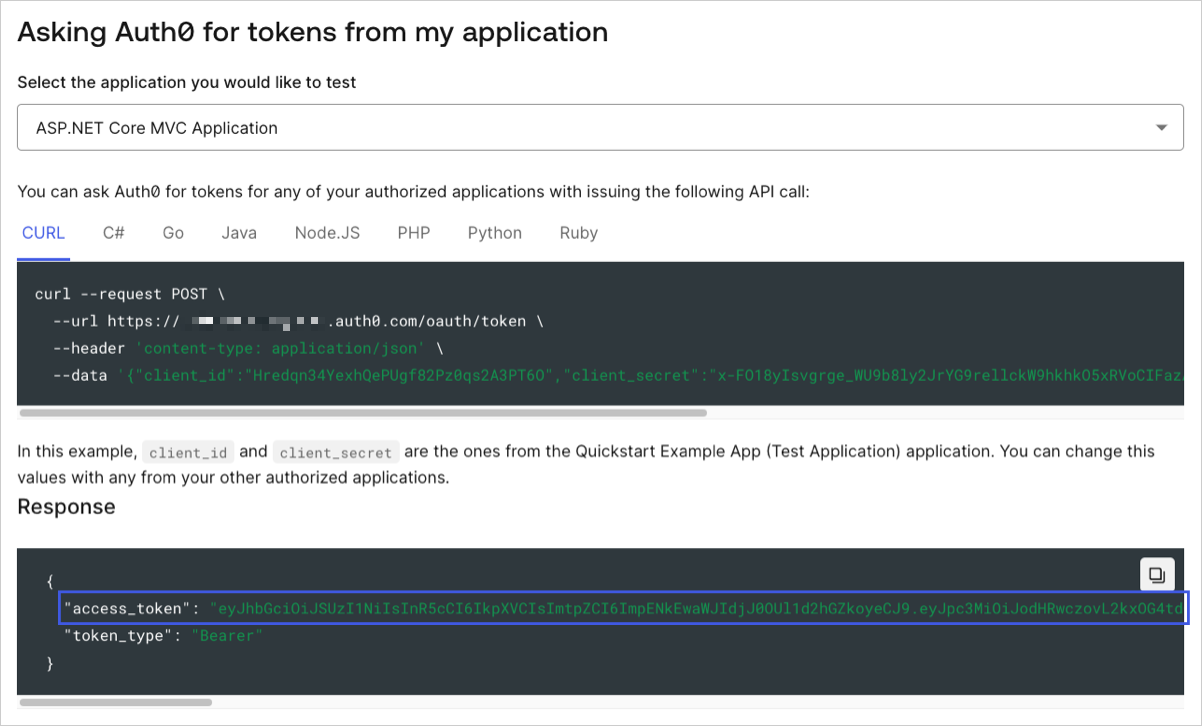 Provide the Access Token as an
Provide the Access Token as an
checkJwt
middleware constructed from express-oauth2-jwt-bearer.You can configure individual routes to look for a particular scope. To achieve that, set up another middleware
with the requiresScope method. Provide the required scopes and apply the middleware to any routes you
want to add authorization to.Pass the checkJwt and requiredScopes middlewares to the route you want to protect.In this configuration, only access tokens with the read:messages scope can access the endpoint.Make a Call to Your API
To make calls to your API, you need an Access Token. You can get an Access Token for testing purposes from the Test view in your API settings.
Authorization header in your requests.Checkpoint
Now that you have configured your application, run your application to verify that:GET /api/publicis available for non-authenticated requests.GET /api/privateis available for authenticated requests.GET /api/private-scopedis available for authenticated requests containing an access token with theread:messagesscope.
Next Steps
Excellent work! If you made it this far, you should now have login, logout, and user profile information running in your application.This concludes our quickstart tutorial, but there is so much more to explore. To learn more about what you can do with Auth0, check out:- Auth0 Dashboard - Learn how to configure and manage your Auth0 tenant and applications
- express-oauth2-jwt-bearer SDK - Explore the SDK used in this tutorial more fully
- Auth0 Marketplace - Discover integrations you can enable to extend Auth0’s functionality


























